價格預言機的使用總結(二):UniswapV2篇
前言
該系列的前一篇文章介紹了 Chainlink 價格預言機的使用,其目前也被大部分 DeFi 應用所使用,但依然存在局限性。首先是所支持的 Token 的覆蓋率還不全,尤其是長尾資產,大多還未支持,比如 SHIB,目前只在 BSC 主網有 SHIB/USD 的 Price Feed,而其它網絡的都還沒有,連 Ethereum 的都還沒支持。其次,有些資產的偏差閾值較大,價格更新也比較慢,可能長達十幾二十個小時才會更新價格,比如 BNT。
這時候就需要考慮其它價格預言機了,而 UniswapV2 和 UniswapV3 都是不錯的選擇。
本篇先來聊聊如何使用 UniswapV2 作為價格預言機。
UniswapV2 價格預言機
UniswapV2 使用的價格預言機稱為 TWAP(Time-Weighted Average Price),即時間加權平均價格。不同於鏈下聚合的 Chainlink 取自多個不同交易所的數據作為數據源,TWAP 的數據源來自於 Uniswap 自身的交易數據,價格的計算也都是在鏈上執行的,因此,TWAP 屬於鏈上預言機。
TWAP 的原理比較簡單,首先,在 UniswapV2Pair 合約中,會存儲兩個變量 price0CumulativeLast 和 price1CumulativeLast,在 _update() 函數中會更新這兩個變量,其相關代碼如下:
contract UniswapV2Pair {
...
uint32 private blockTimestampLast;
uint public price0CumulativeLast;
uint public price1CumulativeLast;
...
// update reserves and, on the first call per block, price accumulators
function _update(uint balance0, uint balance1, uint112 _reserve0, uint112 _reserve1) private {
...
uint32 blockTimestamp = uint32(block.timestamp % 2**32);
uint32 timeElapsed = blockTimestamp - blockTimestampLast;
if (timeElapsed > 0 && _reserve0 != 0 && _reserve1 != 0) {
// * never overflows, and + overflow is desired
price0CumulativeLast += uint(UQ112x112.encode(_reserve1).uqdiv(_reserve0)) * timeElapsed;
price1CumulativeLast += uint(UQ112x112.encode(_reserve0).uqdiv(_reserve1)) * timeElapsed;
}
blockTimestampLast = blockTimestamp;
...
}
}
price0CumulativeLast 和 price1CumulativeLast 分別記錄了 token0 和 token1 的累計價格。所謂累計價格,其代表的是整個合約歷史中每一秒的 Uniswap 價格總和。且只會在每個區塊第一筆交易時執行累加計算,累加的值不是當前區塊的第一筆交易的價格,而是在這之前的最後一筆交易的價格,所以至少也是上個區塊的價格。取自之前區塊的價格,可以大大提高操控價格的成本,所以自然也提高了安全性。
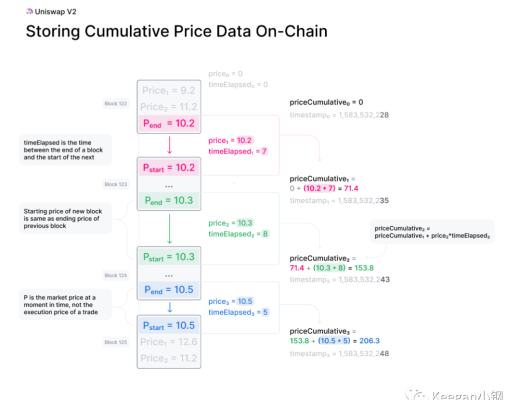
如上圖所示,合約的第一個區塊為 Block 122,這時候,價格和時間差都為 0,所以累計價格也為 0。到了下一個區塊 Block 123,這時候取自上個區塊的最後一口價格 10.2,且經過的時間差為 7,因此就可以計算出累計價格 priceCumulative = 10.2 * 7 = 71.4。再到下個區塊 Block 124,取自上一口價格 10.3,兩個區塊間的時間差為 8,那此時的累計價格就變成了 71.4 + (10.3 * 8) = 153.8。Block 125 的時候也同理,上口價格為 10.5,區塊時間差為 5,所以最新的累計價格就變成了 153.8 + (10.5 * 5) = 206.3。
有了這個基礎之後,就可以計算 TWAP 了。
固定時間窗口 TWAP
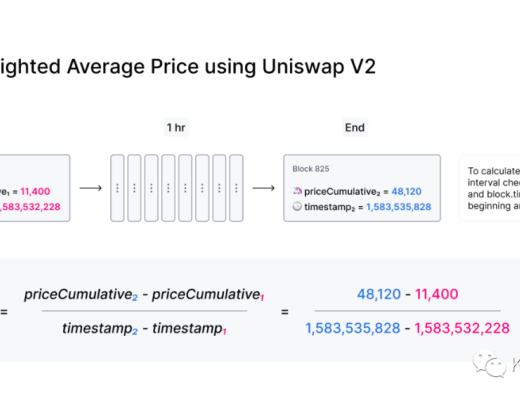
計算 TWAP 的原理也是非常簡單,如上圖所示,這是計算時間間隔為 1 小時的 TWAP,取自开始和結束時的累計價格和兩區塊當時的時間戳,兩者的累計價格相減,再除以兩者之間的時間差,就算出這 1 小時內的 TWAP 價格了。
這是 TWAP 最簡單的計算方式,也稱為固定時間窗口的 TWAP。下面來講講具體如何實現。
Uniswap 官方也有提供了一個示例代碼來計算固定時間窗口的 TWAP,其代碼放在 v2-periphery 項目中:
https://github.com/Uniswap/v2-periphery/blob/master/contracts/examples/ExampleOracleSimple.sol
該示例代碼也比較簡單,我們直接貼上代碼看看:
pragma solidity =0.6.6;
import '@uniswap/v2-core/contracts/interfaces/IUniswapV2Factory.sol';
import '@uniswap/v2-core/contracts/interfaces/IUniswapV2Pair.sol';
import '@uniswap/lib/contracts/libraries/FixedPoint.sol';
import '../libraries/UniswapV2OracleLibrary.sol';
import '../libraries/UniswapV2Library.sol';
// fixed window oracle that recomputes the average price for the entire period once every period
// note that the price average is only guaranteed to be over at least 1 period, but may be over a longer period
contract ExampleOracleSimple {
using FixedPoint for *;
uint public constant PERIOD = 24 hours;
IUniswapV2Pair immutable pair;
address public immutable token0;
address public immutable token1;
uint public price0CumulativeLast;
uint public price1CumulativeLast;
uint32 public blockTimestampLast;
FixedPoint.uq112x112 public price0Average;
FixedPoint.uq112x112 public price1Average;
constructor(address factory, address tokenA, address tokenB) public {
IUniswapV2Pair _pair = IUniswapV2Pair(UniswapV2Library.pairFor(factory, tokenA, tokenB));
pair = _pair;
token0 = _pair.token0();
token1 = _pair.token1();
price0CumulativeLast = _pair.price0CumulativeLast(); // fetch the current accumulated price value (1 / 0)
price1CumulativeLast = _pair.price1CumulativeLast(); // fetch the current accumulated price value (0 / 1)
uint112 reserve0;
uint112 reserve1;
(reserve0, reserve1, blockTimestampLast) = _pair.getReserves();
require(reserve0 != 0 && reserve1 != 0, 'ExampleOracleSimple: NO_RESERVES'); // ensure that there's liquidity in the pair
}
function update() external {
(uint price0Cumulative, uint price1Cumulative, uint32 blockTimestamp) =
UniswapV2OracleLibrary.currentCumulativePrices(address(pair));
uint32 timeElapsed = blockTimestamp - blockTimestampLast; // overflow is desired
// ensure that at least one full period has passed since the last update
require(timeElapsed >= PERIOD, 'ExampleOracleSimple: PERIOD_NOT_ELAPSED');
// overflow is desired, casting never truncates
// cumulative price is in (uq112x112 price * seconds) units so we simply wrap it after division by time elapsed
price0Average = FixedPoint.uq112x112(uint224((price0Cumulative - price0CumulativeLast) / timeElapsed));
price1Average = FixedPoint.uq112x112(uint224((price1Cumulative - price1CumulativeLast) / timeElapsed));
price0CumulativeLast = price0Cumulative;
price1CumulativeLast = price1Cumulative;
blockTimestampLast = blockTimestamp;
}
// note this will always return 0 before update has been called successfully for the first time.
function consult(address token, uint amountIn) external view returns (uint amountOut) {
if (token == token0) {
amountOut = price0Average.mul(amountIn).decode144();
} else {
require(token == token1, 'ExampleOracleSimple: INVALID_TOKEN');
amountOut = price1Average.mul(amountIn).decode144();
}
}
}
PERIOD 指定為了 24 小時,說明這個示例計算 TWAP 的固定時間窗口為 24 小時,即每隔 24 小時才更新一次價格。
該示例也只保存一個交易對的價格,即 token0-token1 的價格。price0Average 和 price1Average 分別就是 token0 和 token1 的 TWAP 價格。比如,token0 為 WETH,token1 為 USDC,那 price0Average 就是 WETH 對 USDC 的價格,而 price1Average 則是 USDC 對 WETH 的價格。
update() 函數就是更新 TWAP 價格的函數,這一般需要鏈下程序的定時任務來觸發,按照這個示例的話,就是鏈下的定時任務需要每隔 24 小時就定時觸發調用 update() 函數。
update() 函數的實現邏輯也和上面所述的公式一致:
讀取出當前最新的累計價格和當前的時間戳;
計算出當前時間和上一次更新價格時的時間差 timeElapsed,要求該時間差需要達 24 小時;
根據公式 TWAP = (priceCumulative - priceCumulativeLast) / timeElapsed 計算得到最新的 TWAP,即 priceAverage;
更新 priceCumulativeLast 和 blockTimestampLast 為當前最新的累計價格和時間戳。
不過,有一點需要注意,因為 priceCumulative 本身計算存儲時是做了左移 112 位的操作的,所以計算所得的 priceAverage 也是左移了 112 位的。
consult() 函數則可查詢出用 TWAP 價格計算可兌換的數量。比如,token0 為 WETH,token1 為 USDC,假設 WETH 的價格為 3000 USDC,查詢 consult() 時,若傳入的參數 token 為 token0 的地址,amountIn 為 2,那輸出的 amountOut 則為 3000 * 2 = 6000,可理解為若支付 2 WETH,就可根據價格換算成 6000 USDC。
滑動時間窗口 TWAP
固定時間窗口 TWAP 的原理和實現,比較簡單,但其最大的不足就是價格變化不夠平滑,時間窗口越長,價格變化就可能會越陡峭。因此,在實際應用中,更多其實是用滑動時間窗口的 TWAP。
所謂滑動時間窗口 TWAP,就是說,計算 TWAP 的時間窗口並非固定的,而是滑動的。這種算法的主要原理就是將時間窗口劃分為多個時間片段,每過一個時間片段,時間窗口就會往右滑動一格,如下圖所示:
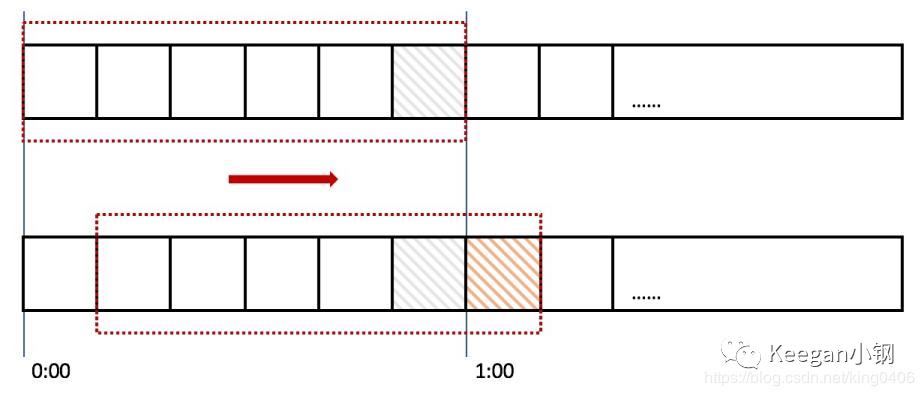
上圖所示的時間窗口為 1 小時,劃分為了 6 個時間片段,每個時間片段則為 10 分鐘。那每過 10 分鐘,整個時間窗口就會往右滑動一格。而計算 TWAP 時的公式則沒有變,依然還是取自時間窗口的起點和終點。如果時間窗口為 24 小時,按照固定時間窗口算法,每隔 24 小時 TWAP 價格才會更新,但使用滑動時間窗口算法後,假設時間片段為 1 小時,則 TWAP 價格是每隔 1 小時就會更新。
Uniswap 官方也同樣提供了這種滑動時間窗口 TWAP 實現的示例代碼,其 Github 地址為:
https://github.com/Uniswap/v2-periphery/blob/master/contracts/examples/ExampleSlidingWindowOracle.sol
我們也貼上代碼看看:
pragma solidity =0.6.6;
import '@uniswap/v2-core/contracts/interfaces/IUniswapV2Factory.sol';
import '@uniswap/v2-core/contracts/interfaces/IUniswapV2Pair.sol';
import '@uniswap/lib/contracts/libraries/FixedPoint.sol';
import '../libraries/SafeMath.sol';
import '../libraries/UniswapV2Library.sol';
import '../libraries/UniswapV2OracleLibrary.sol';
// sliding window oracle that uses observations collected over a window to provide moving price averages in the past
// `windowSize` with a precision of `windowSize / granularity`
// note this is a singleton oracle and only needs to be deployed once per desired parameters, which
// differs from the simple oracle which must be deployed once per pair.
contract ExampleSlidingWindowOracle {
using FixedPoint for *;
using SafeMath for uint;
struct Observation {
uint timestamp;
uint price0Cumulative;
uint price1Cumulative;
}
address public immutable factory;
// the desired amount of time over which the moving average should be computed, e.g. 24 hours
uint public immutable windowSize;
// the number of observations stored for each pair, i.e. how many price observations are stored for the window.
// as granularity increases from 1, more frequent updates are needed, but moving averages become more precise.
// averages are computed over intervals with sizes in the range:
// [windowSize - (windowSize / granularity) * 2, windowSize]
// e.g. if the window size is 24 hours, and the granularity is 24, the oracle will return the average price for
// the period:
// [now - [22 hours, 24 hours], now]
uint8 public immutable granularity;
// this is redundant with granularity and windowSize, but stored for gas savings & informational purposes.
uint public immutable periodSize;
// mapping from pair address to a list of price observations of that pair
mapping(address => Observation[]) public pairObservations;
constructor(address factory_, uint windowSize_, uint8 granularity_) public {
require(granularity_ > 1, 'SlidingWindowOracle: GRANULARITY');
require(
(periodSize = windowSize_ / granularity_) * granularity_ == windowSize_,
'SlidingWindowOracle: WINDOW_NOT_EVENLY_DIVISIBLE'
);
factory = factory_;
windowSize = windowSize_;
granularity = granularity_;
}
// returns the index of the observation corresponding to the given timestamp
function observationIndexOf(uint timestamp) public view returns (uint8 index) {
uint epochPeriod = timestamp / periodSize;
return uint8(epochPeriod % granularity);
}
// returns the observation from the oldest epoch (at the beginning of the window) relative to the current time
function getFirstObservationInWindow(address pair) private view returns (Observation storage firstObservation) {
uint8 observationIndex = observationIndexOf(block.timestamp);
// no overflow issue. if observationIndex + 1 overflows, result is still zero.
uint8 firstObservationIndex = (observationIndex + 1) % granularity;
firstObservation = pairObservations[pair][firstObservationIndex];
}
// update the cumulative price for the observation at the current timestamp. each observation is updated at most
// once per epoch period.
function update(address tokenA, address tokenB) external {
address pair = UniswapV2Library.pairFor(factory, tokenA, tokenB);
// populate the array with empty observations (first call only)
for (uint i = pairObservations[pair].length; i < granularity; i++) {
pairObservations[pair].push();
}
// get the observation for the current period
uint8 observationIndex = observationIndexOf(block.timestamp);
Observation storage observation = pairObservations[pair][observationIndex];
// we only want to commit updates once per period (i.e. windowSize / granularity)
uint timeElapsed = block.timestamp - observation.timestamp;
if (timeElapsed > periodSize) {
(uint price0Cumulative, uint price1Cumulative,) = UniswapV2OracleLibrary.currentCumulativePrices(pair);
observation.timestamp = block.timestamp;
observation.price0Cumulative = price0Cumulative;
observation.price1Cumulative = price1Cumulative;
}
}
// given the cumulative prices of the start and end of a period, and the length of the period, compute the average
// price in terms of how much amount out is received for the amount in
function computeAmountOut(
uint priceCumulativeStart, uint priceCumulativeEnd,
uint timeElapsed, uint amountIn
) private pure returns (uint amountOut) {
// overflow is desired.
FixedPoint.uq112x112 memory priceAverage = FixedPoint.uq112x112(
uint224((priceCumulativeEnd - priceCumulativeStart) / timeElapsed)
);
amountOut = priceAverage.mul(amountIn).decode144();
}
// returns the amount out corresponding to the amount in for a given token using the moving average over the time
// range [now - [windowSize, windowSize - periodSize * 2], now]
// update must have been called for the bucket corresponding to timestamp `now - windowSize`
function consult(address tokenIn, uint amountIn, address tokenOut) external view returns (uint amountOut) {
address pair = UniswapV2Library.pairFor(factory, tokenIn, tokenOut);
Observation storage firstObservation = getFirstObservationInWindow(pair);
uint timeElapsed = block.timestamp - firstObservation.timestamp;
require(timeElapsed <= windowSize, 'SlidingWindowOracle: MISSING_HISTORICAL_OBSERVATION');
// should never happen.
require(timeElapsed >= windowSize - periodSize * 2, 'SlidingWindowOracle: UNEXPECTED_TIME_ELAPSED');
(uint price0Cumulative, uint price1Cumulative,) = UniswapV2OracleLibrary.currentCumulativePrices(pair);
(address token0,) = UniswapV2Library.sortTokens(tokenIn, tokenOut);
if (token0 == tokenIn) {
return computeAmountOut(firstObservation.price0Cumulative, price0Cumulative, timeElapsed, amountIn);
} else {
return computeAmountOut(firstObservation.price1Cumulative, price1Cumulative, timeElapsed, amountIn);
}
}
}
要實現滑動時間窗口算法,就需要將時間分段,還需要保存每個時間段的 priceCumulative。在這實現的示例代碼中,定義了結構體 Observation,用來保存每個時間片段的數據,包括兩個 token 的 priceCumulative 和記錄的時間點 timestamp。還定義了 pairObservations 用來存儲每個 pair 的 Observation 數組,而數組實際的長度取決於將整個時間窗口劃分為多少個時間片段。
windowSize 表示時間窗口大小,比如 24 小時,granularity 是劃分的時間片段數量,比如 24 段,periodSize 則是每時間片段的大小,比如 1 小時,是由 windowSize / granularity 計算所得。這幾個值都在構造函數中進行了初始化。
觸發 update() 函數則更新存儲最新時間片段的 observation,如時間片段大小為 1 小時,即每隔 1 小時就要觸發 update() 函數一次。因為這個示例中是支持多個 pair 的,所以 update() 時需要指定所要更新的兩個 token。
而查詢當前 TWAP 價格的計算就在 consult() 函數裏實現了。首先,先獲取到當前時間窗口裏的第一個時間片段的 observation,也算出當前時間與第一個 observation 時間的時間差,且讀取出當前最新的 priceCumulative,之後就在 computeAmountOut() 函數裏計算得到最新的 TWAP 價格 priceAverage,且根據 amountIn 算出了 amountOut 並返回。
總結
本文我們主要介紹了被廣泛使用的一種鏈上預言機 TWAP(時間加權平均價格),且介紹了固定時間窗口和滑點時間窗口兩種算法的 TWAP。雖然,TWAP 是由 Uniswap 推出的,但因為很多其他 DEX 也採用了和 Uniswap 一樣的底層實現,如 SushiSwap、PancakeSwap 等,所以這些 DEX 也可以用同樣的算法計算出對應的 TWAP。
但使用 UniswapV2 的 TWAP,其主要缺陷就是需要鏈下程序定時觸發 update() 函數,存在維護成本。UniswapV3 的 TWAP 則解決了這個問題,下一篇會來聊聊其具體是如何實現的。
文章首發於「Keegan小鋼」公衆號:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA5OTI1NDE0Mw==&mid=2652494441&idx=1&sn=57a97690390b93770c5a906dce4157c8&chksm=8b685079bc1fd96f9ab60cc1b41b8642abf807a13a37c12f05a280be2e03f3a9288a047b5739&token=1584634265&lang=zh_CN#rd
鄭重聲明:本文版權歸原作者所有,轉載文章僅為傳播信息之目的,不構成任何投資建議,如有侵權行為,請第一時間聯絡我們修改或刪除,多謝。
比特幣跌破9.5萬、以太坊失守3300美元,本週聖誕節市場避險情緒濃厚
比 特幣週六最高從 92,268 美元反彈到 9.95 萬美元之後,又開始一波震盪下跌,撰稿當下最...
24H熱門幣種與要聞 | Michael Saylor發布數字資產框架提案;Azuki疑似即將發幣(12.23)
24 H 熱門幣種 1、CEX 熱門幣種 CEX 成交額 Top 10 及 24 小時漲跌幅: B...
從銘文賽道看AI Agent敘事:有哪些潛在發展演變邏輯和投資機會?
原文作者:Haotian 可能大家都感覺這一輪 AI Agent 敘事推進像極了 23 年以來的銘...
文章匯
文章數量
70粉絲數
0