HOKIE: Introduces the Plookup algorithm
The basic idea
The problem Plookup tries to solve is to prove, given two sets, that elements of one set are in the other. Given two sets t and f, s is the sorted result of f. If the element in T appears at least once in F. To determine whether an element in F is included in T, we only need to compare the set of element differences:
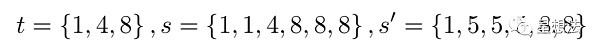
For example, t is the set {1,4,8}, and the difference set of elements is {3, 4}, which are 4-1, 8-4 respectively. If s consists only of elements in t and each element occurs at least once, such as {1,1,4,8,8,8}, the set of differences of elements is also {3,4}. If the elements in S are not exactly elements in T, it does not follow that the elements in S are in the set of T even if the set of element differences is the same. For example, s is {1, 5,5, 5, 8, 8}, and the difference set of elements is {3,4}, 8-5, 5-1, respectively.
A random factor can be introduced to determine the dependency of two sets by adding the preceding and following elements.
Defining polynomial
On the basis of the basic idea, two polynomials F and G are defined:
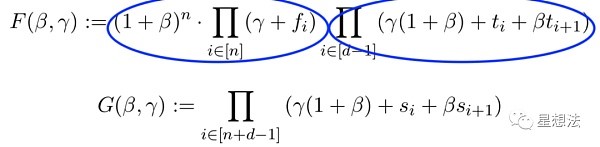
If F and G are equivalent to each other, the following conditions are true:
• F is a member of t
• s is the union of (f, t) and is ordered by the elements in t
If this is true, it follows that the two polynomials are equal. F polynomials can be viewed as having two parts, two serial products. You can view this as a multiplication of the elements in t. You can view this as a multiplication of the elements of f. Since the elements in F belong to t, the multiplication of the elements in F can be imagined as a multiplication of the same elements. Conversely, because of the random factors of beta and gamma, the two conditions satisfied can also be deduced from the F and G equivalents.
On the basis of defining polynomials, the problem can be transformed into two polynomials equal.
Plookup agreement
If you know f and t, you can sort it to get s. Since S is a combination of f and t, s can be represented by two functions, h1 and h2. The key is step 4, which defines the Z function:
• Z(g) = 1 - I started with 1
• Z(x) is the quotient of two polynomials
• Z(g^(n+1)) = 1 - n+1, both polynomials are equal

The verifier, in addition to looking at the Z function, also looks at the H1 / H2 continuity.
conclusion
Plookup proposes a protocol for proving the correctness of a function operation in the case of explicit input/output. The input and output are defined as lookup tables. The calculated input/result is correct as long as it is in the lookup table. Plookup and Plonk adopt the same idea, Plookup defines the polynomial representation of the problem, and proves the recursive representation and boundary of the Z function.
鄭重聲明:本文版權歸原作者所有,轉載文章僅為傳播信息之目的,不構成任何投資建議,如有侵權行為,請第一時間聯絡我們修改或刪除,多謝。
從Treasure到Sharpnel,Web3初創項目燒光融資邁入寒冬
@OdailyChina @XiaMiPP 加密市場,似乎正在經歷一場深刻的寒冬。 就在半年前,我...
Matrixport市場觀察:短期市場情緒波動劇烈,BTC暫守79k支撐位
受美國對等關稅影響,全球資產進入恐慌性拋售階段。BTC 在過去一周走勢相對堅挺但依舊受宏觀因素影響...
一個偉大的創始人應該是什么樣?深度側寫 Paradigm 聯創 Matt Huang
“ 有時我覺得自己在管理 X 战警學院 ”,Matt Huang把他創立的120億美元的加密風投公...
HOKIE交易所
文章數量
31粉絲數
0
評論